CT Scan
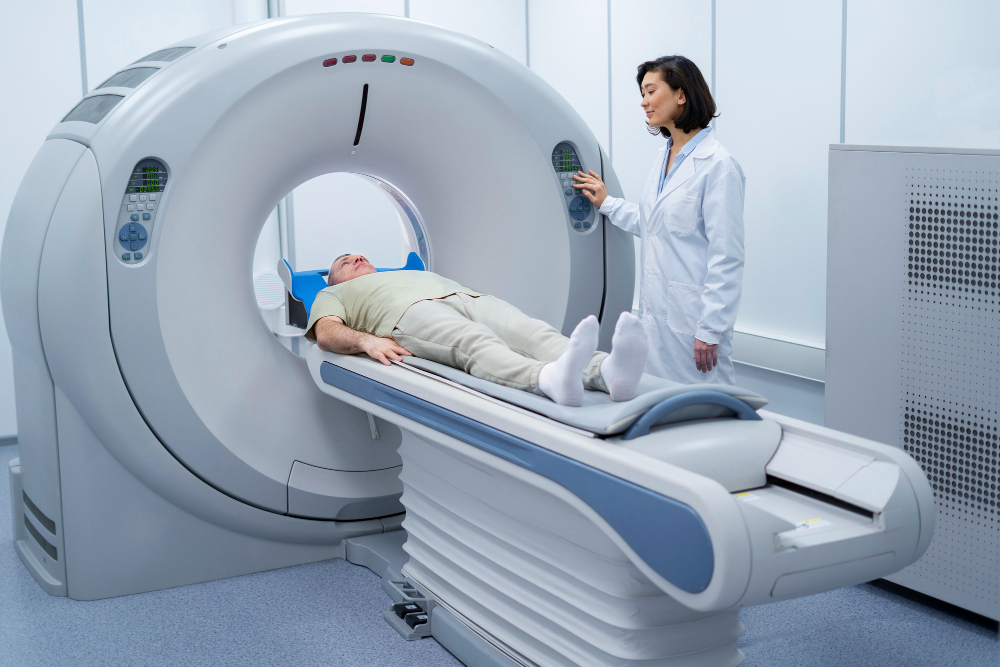
A CT scan, or computed tomography scan, is a medical imaging technique that uses computer-processed combinations of multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles to produce cross-sectional (tomographic) images of specific areas of a scanned object. This technology allows doctors to see inside the body non-invasively and with greater detail than standard X-ray imaging.
CT scans are commonly used to diagnose a variety of conditions and diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, infectious diseases, trauma, and musculoskeletal disorders. The scan can provide detailed images of bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues, which helps in the accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
During a CT scan, the patient typically lies on a table that slides into a large, doughnut-shaped machine. As the patient lies still, the X-ray tube rotates around the body, and the detectors measure the amount of X-rays that pass through the body. These measurements are then used to construct detailed images of the inside of the body.
Factors that may necessitate a CT scan include symptoms like unexplained pain, injury from accidents, or abnormal findings from other tests like X-rays or blood tests. In some cases, a contrast material (a special dye) may be injected into the patient’s bloodstream to highlight specific areas, making the images clearer and more detailed.
CT scans are generally safe, but they do expose patients to a small amount of ionizing radiation. The risk from this radiation is low but is considered in the context of the diagnostic benefit. Special precautions are taken for pregnant women and young children to minimize exposure.
The results from a CT scan can be used to guide further testing or treatments, such as surgery, biopsy, or radiation therapy. They are crucial in emergency situations, providing rapid and detailed information that can be vital for prompt treatment decisions.
Regular maintenance of CT equipment, adherence to safety protocols, and continued advancements in CT technology contribute to the reliability and effectiveness of CT scans in modern medicine.
